Researchers broke down sustainable growth into classes akin to carbon dioxide emissions and use of pure sources like nitrogen, phosphorus and clear water.
Dangerous information, Earthlings: It might be potential for everybody on the planet to reside a “good” life. It might even be potential for people to reside inside their environmental means.
But when current developments proceed, there might be no manner for each of these items to occur on the identical time.
That’s the grim — if not totally shocking — evaluation of researchers from the Sustainability Analysis Institute at College of Leeds in England and the Mercator Analysis Institute on International Commons and Local weather Change in Berlin.
They got here to this conclusion after contemplating 11 vital components of a well-lived existence. Among the objects on their listing are fundamental human wants — revenue of a minimum of $1.90 per day, electrical energy, sufficient meals to eat and a life expectancy of a minimum of 65 years. Others have been social objectives, akin to equality, reliable family and friends, and an honest diploma of life satisfaction (a minimum of 6.5 on a scale of 1 to 10).
The researchers additionally thought of the price to the planet of reaching these items. They broke it down into seven classes akin to carbon dioxide emissions and use of pure sources like nitrogen, phosphorus and clear water.
What they discovered is that humanity has lots of work to do.
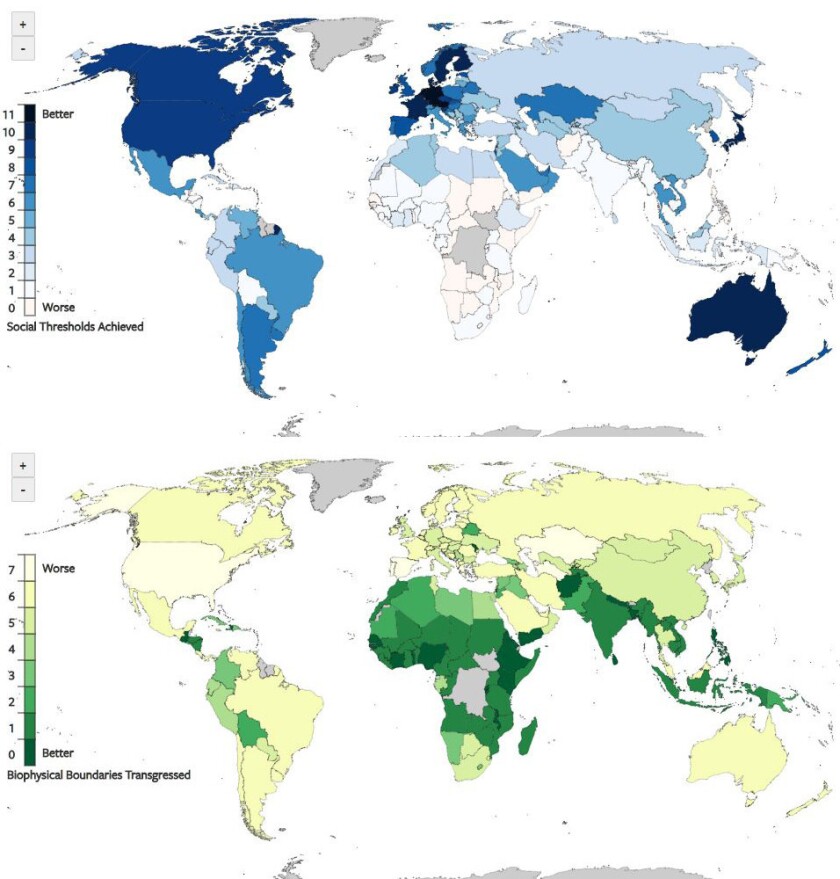
Proper now, there’s not a single nation on Earth that gives its folks a superb, sustainable life.
Not one.
Actually, there aren’t even any that come shut.
The researchers, led by economist Daniel O’Neill of the College of Leeds, consider that is potential to do. However it'll take some onerous work.
Let’s begin with the great life.
Out of roughly 150 nations studied, solely three — Austria, Germany and the Netherlands — at the moment present their residents with all 11 objects on the listing. A further seven — Australia, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Japan and Sweden — supply 10 out of 11. America achieves 9, as does Canada.
However none of them is near doing so sustainably. Certainly, none of them meets greater than two of the seven necessities set out for environmental sustainability.
America doesn’t meet any of them — and misses some “by a large margin,” O’Neill stated. America’s per-capita CO2 emissions are 13 occasions larger than the sustainable degree, its phosphorus use is eight occasions larger and its nitrogen use is seven occasions larger. As if that’s not dangerous sufficient, its ecological and materials footprints are each 4 occasions above sustainable ranges.
On the different finish of the spectrum are 35 nations the place life is fairly depressing. Of the 11 requirements for a superb life, these nations supplied both none or only one.
Basically, the extra social advantages obtainable in a rustic, the extra doubtless that nation resides past its environmental means. The reverse is true as properly — nations that function sustainably have a tendency to supply fewer social advantages.
Maybe the nation that strikes the most effective stability is Vietnam, the researchers stated. Although it meets solely six of 11 social objectives, it meets each sustainability purpose however one. Vietnam’s sole environmental transgression is that it emits an excessive amount of carbon dioxide to maintain the planet from warming by greater than 2 levels Celsius, the purpose set forth within the Paris Settlement.
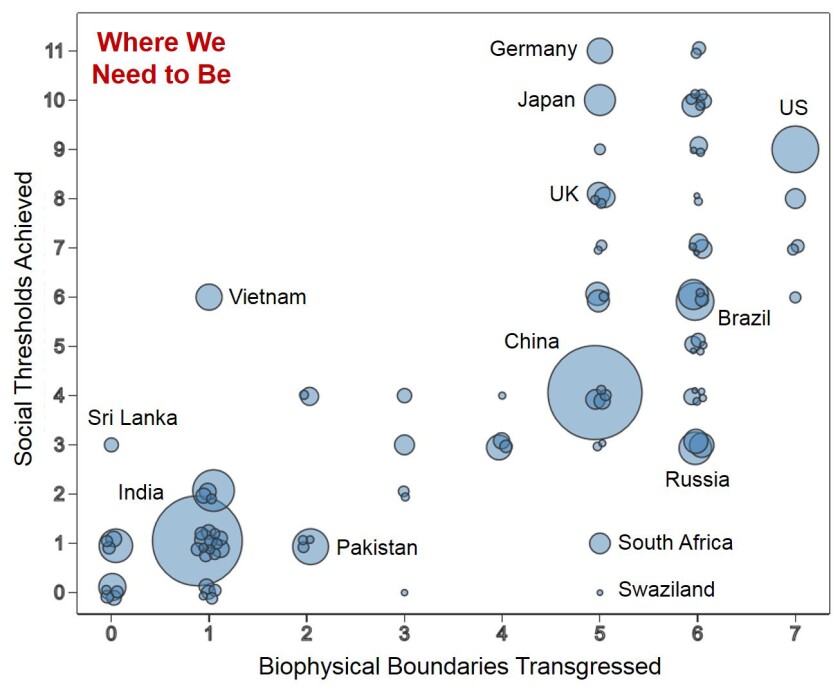
By the identical measures, the nation with the worst stability is Swaziland. This nation is as environmentally unsustainable as China, South Korea and the UK, lacking 5 out of seven objectives. And but, regardless of utilizing so many pure sources, it fails to provide its residents even one of many 11 vital parts of a superb life, the researchers discovered.
All world wide, nations are doing a fairly poor job of dwelling sustainably. Two-thirds of them emit an excessive amount of CO2, and greater than half use an excessive amount of nitrogen and phosphorus. As well as, 56% of nations are utilizing their land in an unsustainable manner.
Solely 16 nations within the evaluation met all seven environmental objectives.
Though the general image could look grim, the researchers noticed some hopeful indicators. For instance, there have been a couple of nations that managed to attain properly for training and life satisfaction whereas holding their CO2 emissions manner beneath the worldwide median degree (that's, the purpose at which half the nations have been emitting extra and half have been emitting much less).
This discovery “demonstrates that rather more carbon-efficient provisioning methods are potential,” O’Neill and his colleagues wrote.
Likewise, the info recommend that the diet, revenue, sanitation and electrical energy wants of every particular person on Earth might be met “with out considerably exceeding planetary boundaries” for sustainability, they wrote.
If somebody might wave a magic wand and reallocate Earth’s sources in order that they have been shared equally by everybody, it will most likely be sufficient to fulfill everybody’s fundamental human wants (the listing that features sufficient meals to eat and sufficient cash to keep away from excessive poverty, amongst different issues), O’Neill stated.
But it surely nonetheless wouldn’t permit everybody to take pleasure in “extra aspirational objectives like secondary training and excessive life satisfaction,” he added. For that, “we have to change into two to 6 occasions extra environment friendly at reworking useful resource use into human well-being.”
That’s a lot simpler stated than carried out, in fact. And it will get solely tougher when you think about that there might be 11.2 billion folks on the planet by the tip of the century, in response to projections from the United Nations.
In concept, rich nations might lower manner again on their useful resource use whereas sustaining their achievements on the social entrance. Some simple first steps embrace “switching from fossil fuels to renewable power, producing merchandise with longer lifetimes, decreasing pointless waste, shifting from animal to crop merchandise, and investing in new applied sciences,” the researchers wrote.
And in a future world “with very totally different social preparations or applied sciences,” there might be a unique equation for changing pure sources into human well-being that enables everybody to take pleasure in all features of the great life, O’Neill stated.
“Is that this real looking?” he stated. “I hope so, as a result of the choice might be environmental disaster.”
The research was printed Monday within the journal Nature Sustainability. You'll be able to discover the outcomes and see the trade-offs for your self on this interactive web site.
Observe me on Twitter @LATkarenkaplan and “like” Los Angeles Instances Science & Well being on Fb.
MORE IN SCIENCE
Radiation from cellphones is just not hazardous to your well being, authorities scientists say
Why diets backfire: A 12 months or extra after weight reduction, the will to eat grows stronger
Post a Comment